The last couple of years have illustrated an interesting labor market, to say the least. In particular, economic behavioral changes among workforce demographics have become the spotlight. While everyone has been effected in some way, shape, or form by changes in recent employment dynamics, Gen Z is outpacing the previous youth employment of Millennials. While many factors can be attributed to this phenomena, they appear to be rooted in the demand side of the labor market - demand for Gen Z workers is higher now than when Millennials faced multi-recession labor markets in their youth.
While being a more streamlined setting than today’s employment landscape, MobLab’s Simple Labor Market enables students to experience what it’s like to be a worker and seek (or decline) work in a competitive labor market.
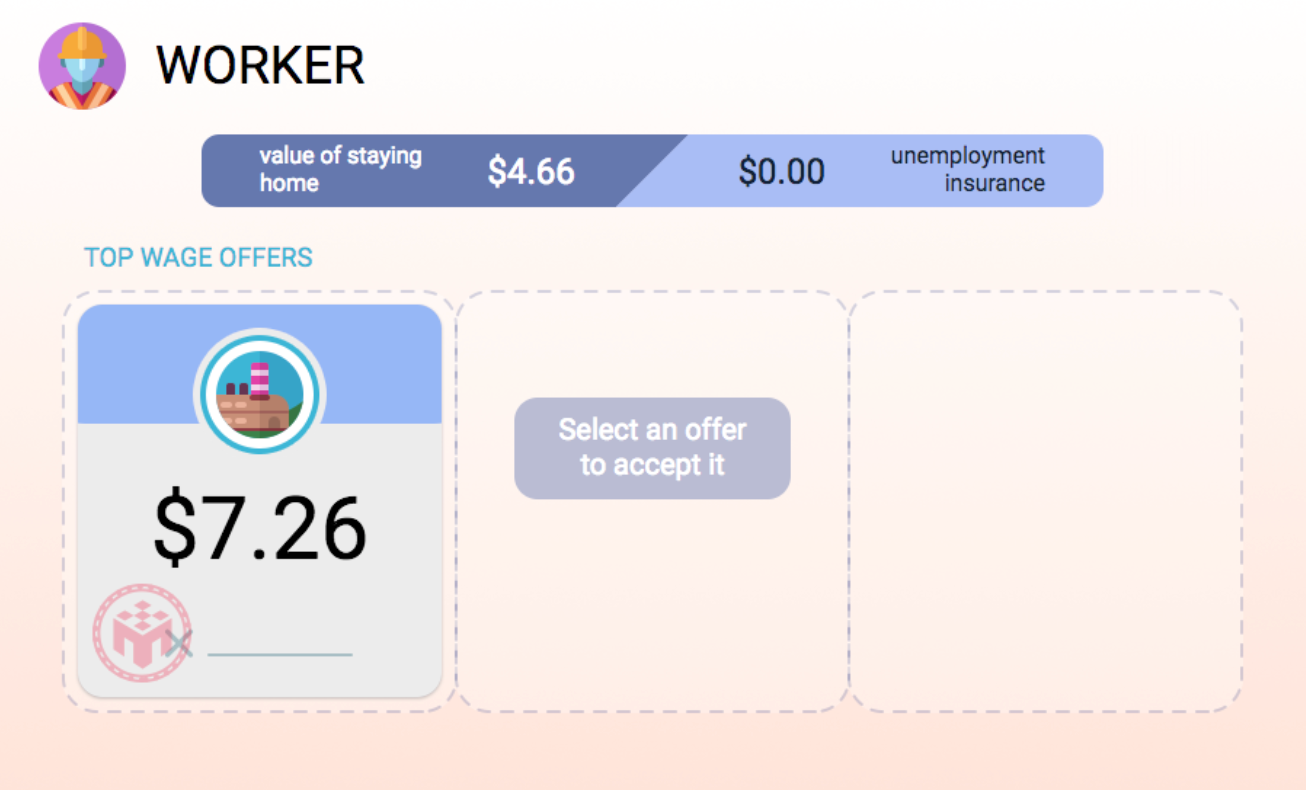
At what price will accepting a job offer as a worker be worthwhile?
In addition, students can experience what it’s like to be an employer at a firm by posting job offers and wages.
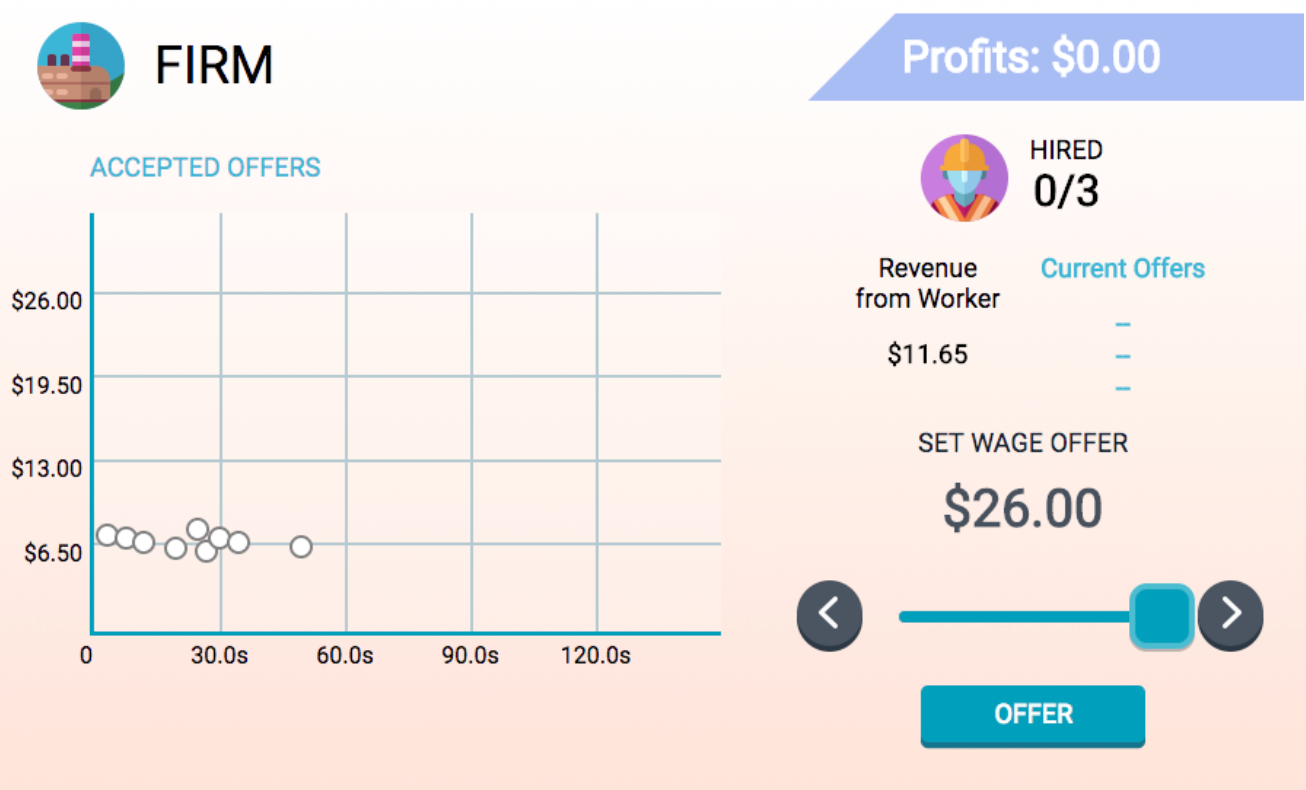
Students can play the role of the Firm and decide what wages they will offer to workers.
For an added real-world twist that highlights government policy making decisions, unemployment insurance can be factored into gameplay.
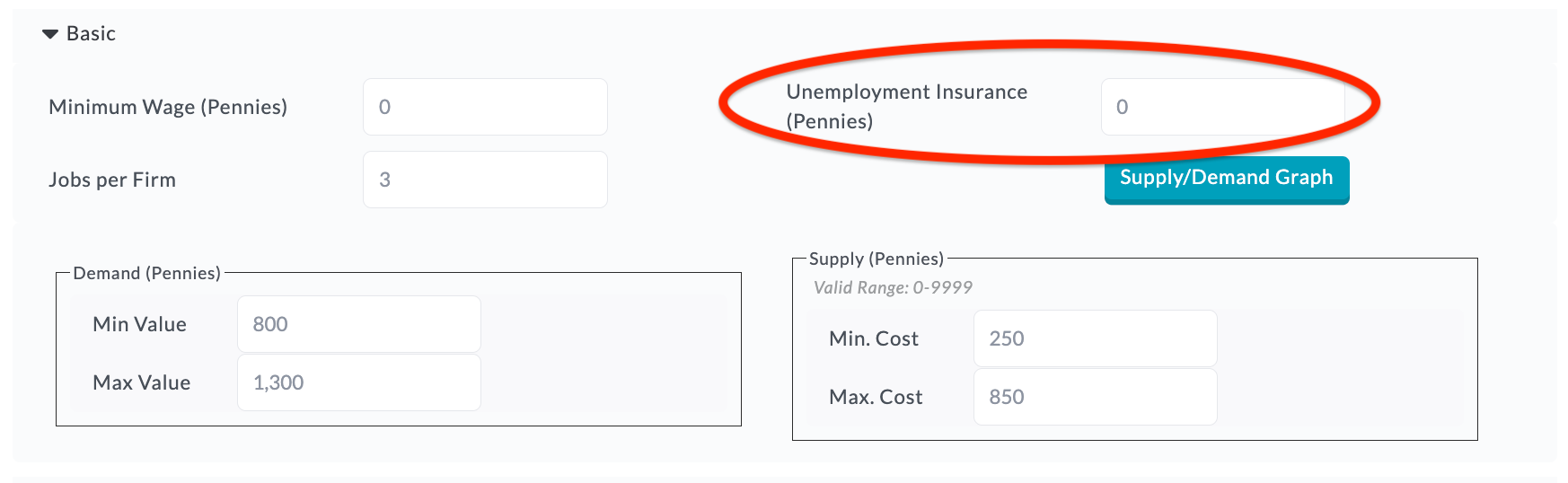
Simulate government policy decisions by changing how much unemployment insurance is offered to the labor market.
In this blog post, we’ll focus specifically on how changing the amount of unemployment insurance causes a leftward shift in the supply of labor. Even though implementing unemployment insurance policy changes doesn’t fully address all the nuances in today’s labor market faced by Gen Z and Millennials, it’s a good way to engage students in discussion about recent events in today’s labor market that they may (or may soon) be experiencing.
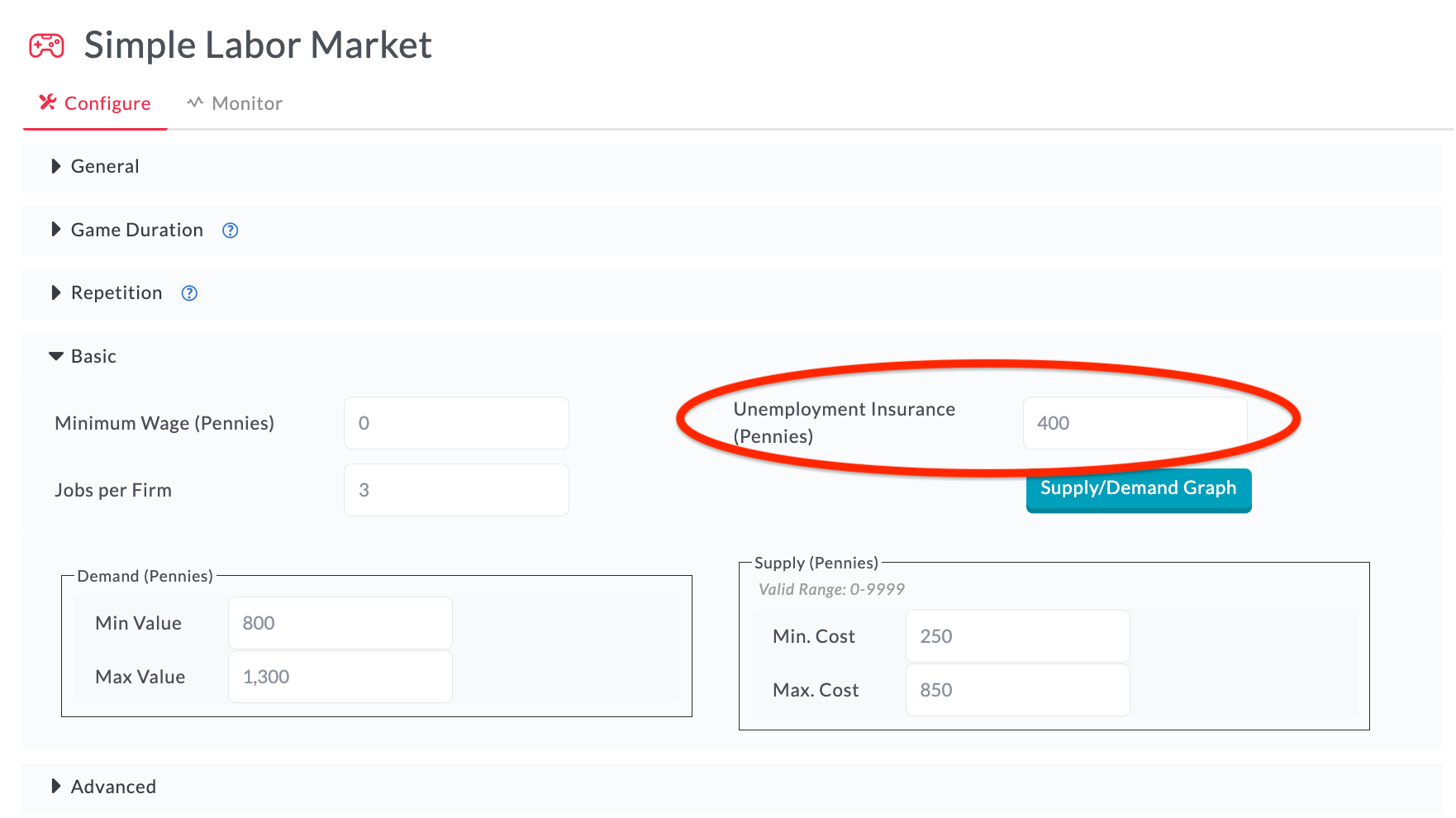
Here we're setting the Unemployment Insurance amount to $4.00 (400 pennies).
By setting the Unemployment Insurance amount above to $4.00, this will result in a higher wages offered in the market and a leftward shift in the supply of labor. How does this change in game parameters relate to a real world example? You may use this treatment variation to simulate the early phases of the COVID-19 outbreak when policy makers increased the amount of unemployment insurance substantially, which contributed to higher wage increases and less supply of labor.
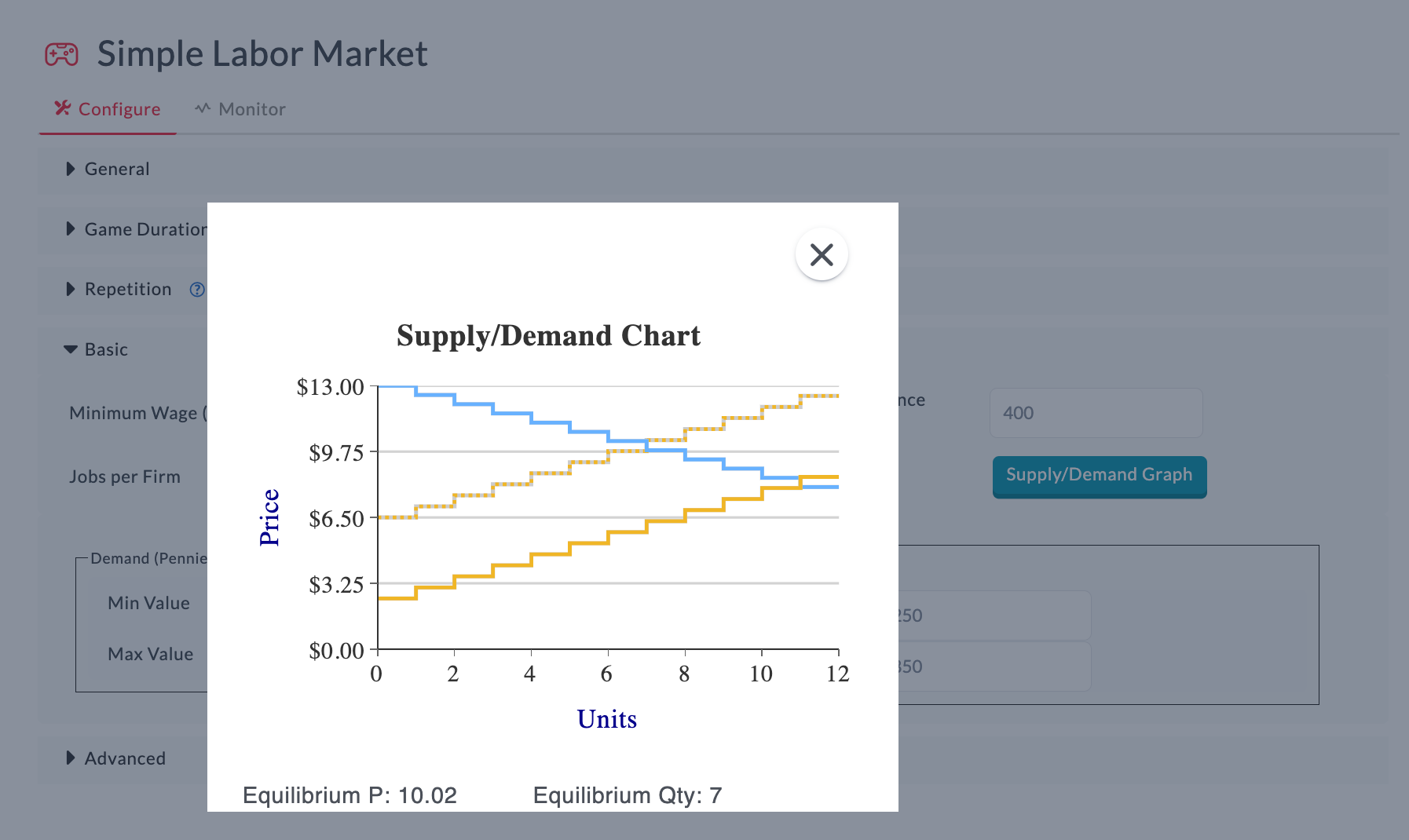
Example of real world labor market policy effects simulated within MobLab's Simple Labor Market game - the result is a leftward shift in the supply curve for labor. Instructors can preview changes in the supply and demand curves for labor based on different Unemployment Insurance amounts in the Configure tab.
As we can see in the game’s results, implementing a policy of $4 Unemployment Insurance has caused high levels of unemployment and an increased equilibrium wage.
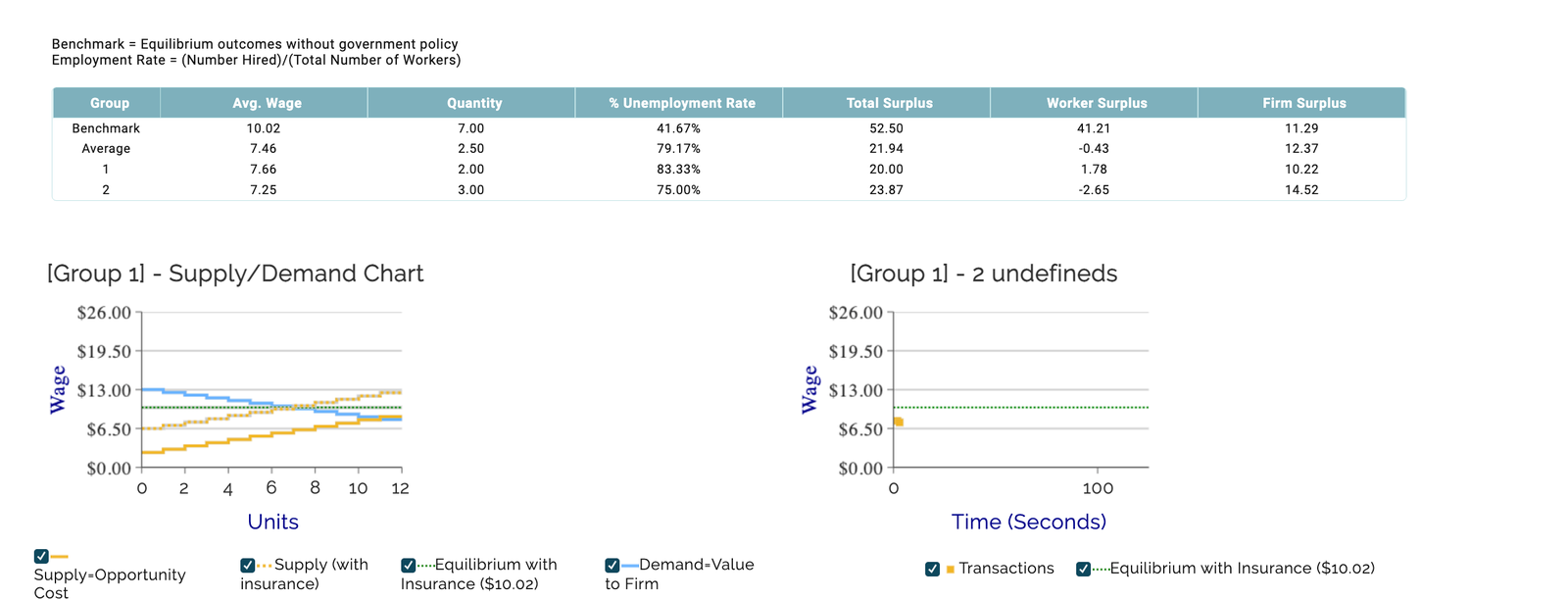
Not too many job takers in this labor market due to implementing large ($4) Unemployment Insurance payments.
Finally, instructors can enable Chat during gameplay so students simulating the roles of Workers and Firms can negotiate wages. In the real world, most job seekers will negotiate their wages with prospective employers. Enabling this feature will help enable more classroom participation and discussion.
MobLab’s Simple Labor Market game is a fun interactive way to allow your students to experience what it’s like to be both a firm and a worker in today’s challenging employment environment. In particular, it can help encourage meaningful discussion about how different demographic groups, such as Gen Z and Millennials, are navigating real-world complexities in the labor market in tandem with government policy decisions.
Want to check out more games for teaching labor markets, business economics, and government policy? Get in touch and we would be happy to give you a personalized tour of the MobLab economics game platform.
While being a more streamlined setting than today’s employment landscape, MobLab’s Simple Labor Market enables students to experience what it’s like to be a worker and seek (or decline) work in a competitive labor market.

At what price will accepting a job offer as a worker be worthwhile?

Students can play the role of the Firm and decide what wages they will offer to workers.

Simulate government policy decisions by changing how much unemployment insurance is offered to the labor market.
Use Case - Unemployment Insurance
In this blog post, we’ll focus specifically on how changing the amount of unemployment insurance causes a leftward shift in the supply of labor. Even though implementing unemployment insurance policy changes doesn’t fully address all the nuances in today’s labor market faced by Gen Z and Millennials, it’s a good way to engage students in discussion about recent events in today’s labor market that they may (or may soon) be experiencing.

Here we're setting the Unemployment Insurance amount to $4.00 (400 pennies).

Example of real world labor market policy effects simulated within MobLab's Simple Labor Market game - the result is a leftward shift in the supply curve for labor. Instructors can preview changes in the supply and demand curves for labor based on different Unemployment Insurance amounts in the Configure tab.

Not too many job takers in this labor market due to implementing large ($4) Unemployment Insurance payments.
MobLab’s Simple Labor Market game is a fun interactive way to allow your students to experience what it’s like to be both a firm and a worker in today’s challenging employment environment. In particular, it can help encourage meaningful discussion about how different demographic groups, such as Gen Z and Millennials, are navigating real-world complexities in the labor market in tandem with government policy decisions.
Want to check out more games for teaching labor markets, business economics, and government policy? Get in touch and we would be happy to give you a personalized tour of the MobLab economics game platform.

